Create a Digital Object Using Spore Protocol
Tutorial Overview
- An IDE/Editor that supports TypeScript
- CKB dev environment: OffCKB
Spore Protocol on CKB
Spore is an on-chain digital object (DOB) protocol backed by CKB. An "on-chain" asset refers to a digital asset whose data is directly encoded onto the blockchain. A Spore Cell can hold any type of assets users want to store on-chain, the following data structure is used in the Spore Cell:
data:
content-type: Bytes # String Bytes
content: Bytes
# OPTIONAL
cluster_id: Bytes
type:
hash_type: "data1"
code_hash: SPORE_TYPE_DATA_HASH
args: SPORE_ID
lock:
<user_defined>
Notice that the data field of the Spore Cell contains content-type and content, which allow users to turn any content form into a digital object. All the fields in a Spore Cell are immutable once created.
In this tutorial, we will build a simple dApp to turn a picture on your computer into a digital object on the blockchain using the Spore SDK.
Setup Devnet & Run Example
Step 1: Initialize
After installing @offckb/cli, run the following command to initlize a project with our built-in templates.
offckb init <project-name>
When prompted to select a dApp template, use your arrow keys to select Create a Digital Object Using Spore Protocol for this tutorial.
- Command
- Response
? Select a dApp template (Use arrow keys)
View and Transfer a CKB Balance
Write an On-Chain Message
Create a Fungible Token
> Create a Digital Object Using Spore Protocol
a simple dApp to create on-chain digital object with spore scripts
init CKB dApp project: /Users/ckb/Desktop/offckb/<project-name>
✨ Done in 2.52s.
Step 2: Start the Devnet
To interact with the dApp, you need to have your Devnet running. Open one terminal and start the Devnet:
- Command
- Response
offckb node
/bin/sh: /Users/nervosDocs/.nvm/versions/node/v18.12.1/lib/node_modules/@offckb/cli/target/ckb/ckb: No such file or directory
/Users/nervosDocs/.nvm/versions/node/v18.12.1/lib/node_modules/@offckb/cli/target/ckb/ckb not found, download and install the new version 0.113.1..
CKB installed successfully.
init Devnet config folder: /Users/nervosDocs/.nvm/versions/node/v18.12.1/lib/node_modules/@offckb/cli/target/devnet
modified /Users/nervosDocs/.nvm/versions/node/v18.12.1/lib/node_modules/@offckb/cli/target/devnet/ckb-miner.toml
CKB output: 2024-03-20 07:56:44.765 +00:00 main INFO sentry sentry is disabled
CKB output: 2024-03-20 07:56:44.766 +00:00 main INFO ckb_bin::helper raise_fd_limit newly-increased limit: 61440
CKB output: 2024-03-20 07:56:44.854 +00:00 main INFO ckb_bin::subcommand::run ckb version: 0.113.1 (95ad24b 2024-01-31)
CKB output: 2024-03-20 07:56:45.320 +00:00 main INFO ckb_db_migration Init database version 20230206163640
CKB output: 2024-03-20 07:56:45.329 +00:00 main INFO ckb_launcher Touch chain spec hash: Byte32(0x3036c73473a371f3aa61c588c38924a93fb8513e481fa7c8d884fc4cf5fd368a)
You might want to check pre-funded accounts and copy private keys for later use. Open another terminal and execute:
- Command
- Response
offckb accounts
Print account list, each account is funded with 42_000_000_00000000 capacity in the genesis block.
[
{
privkey: '0x6109170b275a09ad54877b82f7d9930f88cab5717d484fb4741ae9d1dd078cd6',
pubkey: '0x02025fa7b61b2365aa459807b84df065f1949d58c0ae590ff22dd2595157bffefa',
lockScript: {
codeHash: '0x9bd7e06f3ecf4be0f2fcd2188b23f1b9fcc88e5d4b65a8637b17723bbda3cce8',
hashType: 'type',
args: '0x8e42b1999f265a0078503c4acec4d5e134534297'
},
address: 'ckt1qzda0cr08m85hc8jlnfp3zer7xulejywt49kt2rr0vthywaa50xwsqvwg2cen8extgq8s5puft8vf40px3f599cytcyd8',
args: '0x8e42b1999f265a0078503c4acec4d5e134534297'
},
{
privkey: '0x9f315d5a9618a39fdc487c7a67a8581d40b045bd7a42d83648ca80ef3b2cb4a1',
pubkey: '0x026efa0579f09cc7c1129b78544f70098c90b2ab155c10746316f945829c034a2d',
lockScript: {
codeHash: '0x9bd7e06f3ecf4be0f2fcd2188b23f1b9fcc88e5d4b65a8637b17723bbda3cce8',
hashType: 'type',
args: '0x758d311c8483e0602dfad7b69d9053e3f917457d'
},
address: 'ckt1qzda0cr08m85hc8jlnfp3zer7xulejywt49kt2rr0vthywaa50xwsqt435c3epyrupszm7khk6weq5lrlyt52lg48ucew',
args: '0x758d311c8483e0602dfad7b69d9053e3f917457d'
},
#...
]
Step 3: Run the Example
Navigate to your project, install the node dependencies, and start running the example:
- Command
- Response
cd <project-name> && yarn && yarn start
$ parcel index.html
Server running at http://localhost:1234
✨ Built in 66ms
Now, the app is running in http://localhost:1234
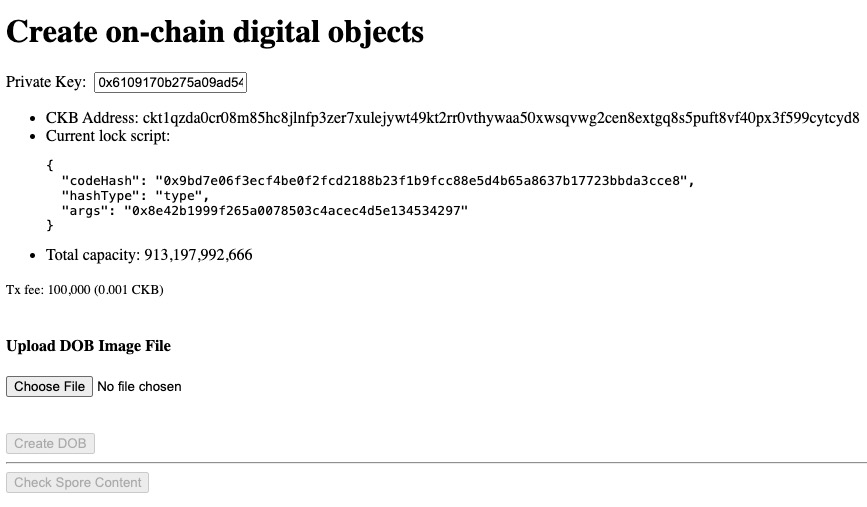
Behind the Scene
Open the lib.ts file in your project, it lists all the important functions that do the most of work for the project.
Create Digital Object
Check out the createSporeDOB function:
export async function createSporeDOB(
privkey: string,
content: Uint8Array
): Promise<{ txHash: string; outputIndex: number }>;
It accepts two parameters,
- the private key that is used to sign and create the digital object
- the content to be stored in the digital object.
The content can be any type of data that is serialized into a Uint8Array. Here we are dealing with images, so the content is the result of FileReader.readAsArrayBuffer. You can check out the following code recipe in handleFileChange function from the react frontend index.tsx:
const reader = new FileReader();
reader.onload = () => {
// Access the file content here
const content = reader.result;
if (content && content instanceof ArrayBuffer) {
const uint8Array = new Uint8Array(content);
setFileContent(uint8Array);
}
};
// Read the file as ArrayBuffer
reader.readAsArrayBuffer(files[0]);
Once we have the picture content and the private key, we will build a transaction that produces a Spore output Cell, aka the digital object Cell. We can handle all the logic with Lumos.js, but with the help of Spore-SDK, it becomes very simple to do:
export async function createSporeDOB(
privkey: string,
content: Uint8Array
): Promise<{ txHash: string; outputIndex: number }> {
const wallet = createDefaultLockWallet(privkey);
const { txSkeleton, outputIndex } = await createSpore({
data: {
contentType: "image/jpeg",
content,
},
toLock: wallet.lock,
fromInfos: [wallet.address],
config: SPORE_CONFIG,
});
const txHash = await wallet.signAndSendTransaction(txSkeleton);
console.log(`Spore created at transaction: ${txHash}`);
console.log(
`Spore ID: ${
txSkeleton.get("outputs").get(outputIndex)!.cellOutput.type!.args
}`
);
return { txHash, outputIndex };
}
Notice that the createDefaultLockWallet and const txHash = await wallet.signAndSendTransaction(txSkeleton); are just some methods that helps us to keep the code clean, all it does is the same as the previous tutorials involving signing and sending transactions.
Render Content from Digital Object
Once we created our digital object on-chain, what we love to do is to render and show this digital object. To do this, we need to first find the Spore Cell of our digital object and extract the data from the Spore Cell and decode the content from the data to render it in the browser.
Check out the showSporeContent function:
export async function showSporeContent(txHash: string, index = 0) {
const indexHex = "0x" + index.toString(16);
const { cell } = await rpc.getLiveCell({ txHash, index: indexHex }, true);
if (cell == null) {
return alert("Cell not found, please retry later");
}
const data = cell.data.content;
const msg = unpackToRawSporeData(data);
console.log("Spore data: ", msg);
return msg;
}
We locate the Spore Cell by accepting a outpoint parameter(txHash and outputIndex), and use rpc.getLiveCell to get the Live Cell. Then we unpack the data content from this Cell:
const data = cell.data.content;
const msg = unpackToRawSporeData(data);
To render the image from this raw data, check out the renderSpore function in the index.tsx:
const renderSpore = async () => {
const res = await showSporeContent(txHash, outputIndex);
if (!res) return;
setRawSporeData(res);
// Create Blob from binary data
const buffer = hexStringToUint8Array(res.content.toString().slice(2));
const blob = new Blob([buffer], { type: res.contentType });
const url = URL.createObjectURL(blob);
setImageURL(url);
};
...
{imageURL && <img src={imageURL} />}
Congratulations!
By following this tutorial this far, you have mastered how digital-object works on CKB. Here's a quick recap:
- How Spore protocol works on CKB
- Create an on-chain digital object with a picture via Spore-SDK
- Render the picture in the browser from your digital object
Next Step
So now your app works great on the local blockchain, you might want to switch it to different environments like Testnet and Mainnet.
To do this, you need to update the chain config and related code.
Open the ckb.ts in your project root dir, change the lumosConfig and CKB_RPC_URL:
//export const lumosConfig: config.Config = devConfig as config.Config;
export const lumosConfig = config.predefined.AGGRON4 as config.Config;
//export const CKB_RPC_URL = 'http://localhost:8114';
export const CKB_RPC_URL = "https://testnet.ckb.dev/rpc";
Actually, we have the corresponding Testnet version examples for all these tutorials. The source code of the Testnet version is in https://github.com/nervosnetwork/docs.nervos.org/tree/develop/examples, you can clone the repo and start running on Testnet.
git clone https://github.com/nervosnetwork/docs.nervos.org.git
cd docs.nervos.org/examples/<example-name>
yarn && yarn start
For more details, check out the README.md;
Additional Resources
- Spore protocol: docs.spore.pro
- CKB transaction structure: RFC-0022-transaction-structure
- CKB data structure basics: RFC-0019-data-structure